Objective:-
- Prescriptive analytics aims to identify the best course of action for a given situation, leading to improved results in terms of efficiency, profitability, or other desired metrics.
- By analyzing data and predicting potential problems, prescriptive analytics recommends actions to minimize negative impacts and safeguard against future issues.
Introduction:
In today’s data-driven world, businesses seek to not only understand past performance but also optimize future decisions. Prescriptive modeling bridges the gap between causes and effects, providing actionable recommendations based on advanced analytics for optimal outcomes.
Prescriptive modeling employs mathematical algorithms to recommend optimal actions for specific objectives, surpassing descriptive and predictive analytics. It provides actionable insights on actions to maximize desired outcomes, distinguishing itself with its focus on guiding decision-making processes.
Importance:
- Data-Driven Decisions: Moves beyond intuition and guesswork, suggesting actions based on analyzed data for better decision-making.
- Proactive Problem Solving: Analyzes trends and anticipates potential issues, allowing proactive measures to mitigate risks.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Recommends optimal resource allocation, streamlining processes and maximizing output with fewer resources.
Process:
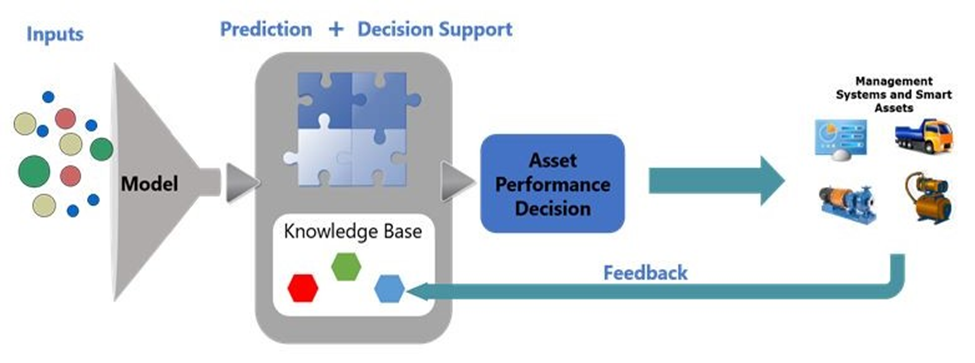
- Problem Formulation: Clearly define the decision problem, objectives, constraints, and decision variables.
- Model Development: Develop mathematical models, such as linear programming, integer programming, or simulation, based on the problem formulation.
- Solution Generation: Use optimization algorithms or simulation techniques to generate optimal or near-optimal solutions.
- Validation and Sensitivity Analysis: Validate the model outputs, assess the robustness of the solutions, and conduct sensitivity analysis to understand the impact of changes in inputs or assumptions.
- Decision Implementation: Translate the recommended actions into operational decisions, monitor performance, and adjust strategies as needed.
Applications:-
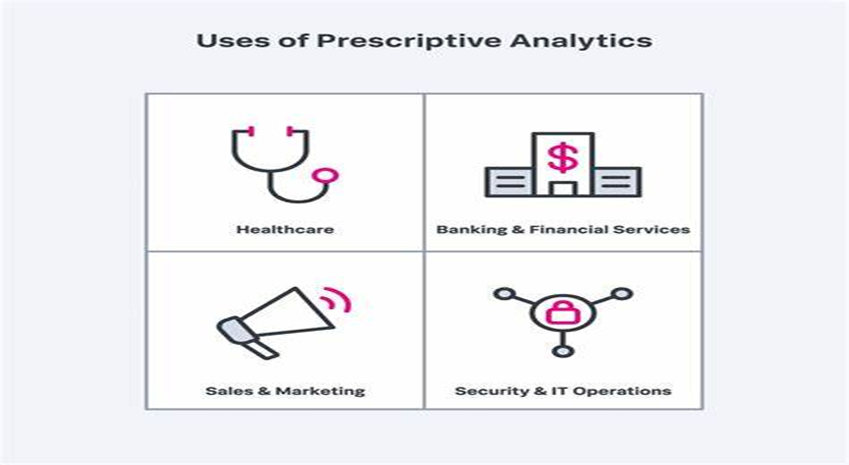
- Healthcare: Enhances resource allocation, treatment plans, and patient scheduling, improving outcomes and operational efficiency for healthcare providers.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizes inventory, routes, and production schedules, reducing costs and improving service levels in supply chain operations.
- Finance: Facilitates portfolio optimization, risk management, and fraud detection, supporting better investment decisions and regulatory compliance for financial institutions.
- Manufacturing: Prescriptive analysis recommends optimal production settings based on real-time data, minimizing waste and maximizing output.
- Retail: Analyzes customer behavior to predict demand and suggest targeted promotions, optimizing inventory and boosting sales.
Advantages:-
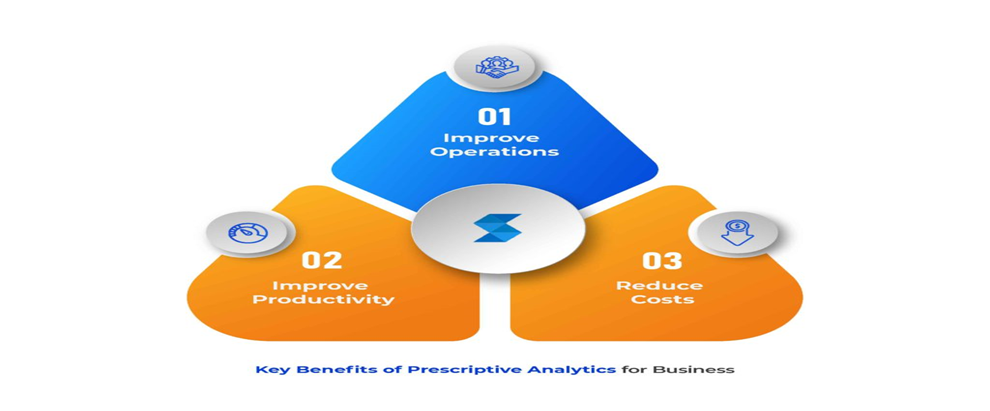
- Optimal Decision Making: Prescriptive modeling guides businesses to decisions maximizing outcomes like profitability, efficiency, or customer satisfaction.
- Resource Allocation: Considering constraints, it aids effective resource allocation to achieve strategic objectives.
- Risk Management: Evaluating risks, it identifies mitigation strategies to minimize adverse impacts on decision outcomes.
- Cybersecurity: Identifies vulnerabilities, prescribes mitigation strategies, and prevents attacks, safeguarding critical systems.
Conclusion
Prescriptive modeling offers a strategic advantage to businesses by providing actionable insights to drive optimal decision-making. With the ability to recommend the best course of action in complex and uncertain environments, prescriptive modeling empowers organizations across industries to achieve their objectives efficiently and effectively


