Objective
Large Language Models (LLMs) revolutionize document summarization by automatically generating concise and informative summaries of lengthy texts. This empowers users to quickly grasp key points, improve information retrieval, and streamline knowledge processing.
Introduction
The vast amount of textual information available today necessitates efficient methods for extracting essential content. Traditional summarization techniques often lack scalability or struggle with complex documents. LLMs offer a powerful solution for overcoming these limitations.
Importance
- Enhanced Information Retrieval: Quickly identify relevant documents within large datasets based on LLM-generated summaries.
- Improved Knowledge Processing: Gain a comprehensive understanding of complex texts or research papers through concise summaries.
- Increased Efficiency: Save time by rapidly grasping key points from lengthy documents, allowing for faster decision-making or research.
Process
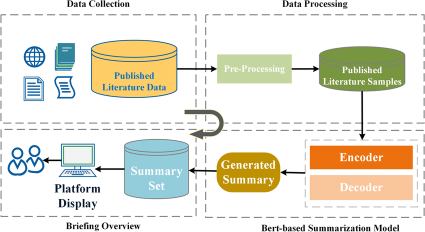
- Document Preprocessing: Prepare documents for LLM processing by cleaning text, removing irrelevant information, and ensuring proper formatting.
- Input Encoding: The prepared data is then encoded to create a numerical representation that the LLM can comprehend. This encoding step is crucial for translating textual information into a format suitable for the model’s processing.
- Summarization Model Application: Once encoded, the data is fed into the LLM, which utilizes its pre-trained knowledge to identify key information, understand context, and generate concise summaries. This step involves the model predicting the most relevant and informative content based on the given input.
- Output Decoding: The generated summary is decoded back into human-readable text for presentation. This step ensures that the summarization output is coherent, grammatically sound, and effectively conveys the essence of the original document.
- Human Review & Refinement: While LLMs generate summaries, human experts may review and refine them to ensure accuracy, clarity, and adherence to specific summarization goals.
Applications
- Research Paper Analysis: Researchers use LLM summaries to quickly understand a collection of research papers, identifying relevant ones for deeper investigation.
- News Article Compilation: News outlets leverage LLMs to generate summaries of daily news articles, allowing users to stay informed on current events without reading every detail.
- Legal Document Review: Lawyers utilize LLM summaries to efficiently grasp the key points of lengthy legal documents, facilitating faster case preparation and analysis.
Advantages
- Scalability: Summarize large volumes of documents efficiently, enabling faster information processing and analysis.
- Improved Accuracy: LLMs are trained on massive datasets, leading to increasingly accurate and comprehensive summaries.
- Flexibility: Generate summaries tailored to specific needs, ranging from short factual summaries to more elaborate content overviews.
Conclusion
LLM-powered document summarization transforms how we interact with textual information. By extracting crucial insights at scale, LLMs empower users to navigate vast information landscapes efficiently, fostering knowledge discovery and informed decision-making. As LLM technology advances, even more sophisticated and nuanced summarization capabilities can be expected.


